用 async/await 来处理异步
async的用法
它作为一个关键字放到函数前面
async function timeout() {
return 'hello world';
}返回一个promise 对象
只有一个作用, 它的调用会返回一个promise 对象。调用一下看看就知道了,怎么调用?async 函数也是函数,所以它的调用和普通函数的调用没有什么区别,直接加括号调用就可以了,为了看结果,console.log 一下
async function timeout() {
return 'hello world'
}
console.log(timeout());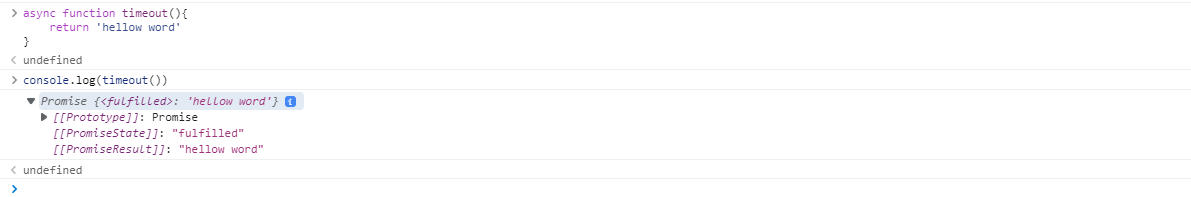
async函数(timeout)的调用,确实返回promise 对象,并且Promise 还有status和value
如果async 函数中有返回值 ,当调用该函数时,内部会调用Promise.solve() 方法把它转化成一个promise 对象作为返回
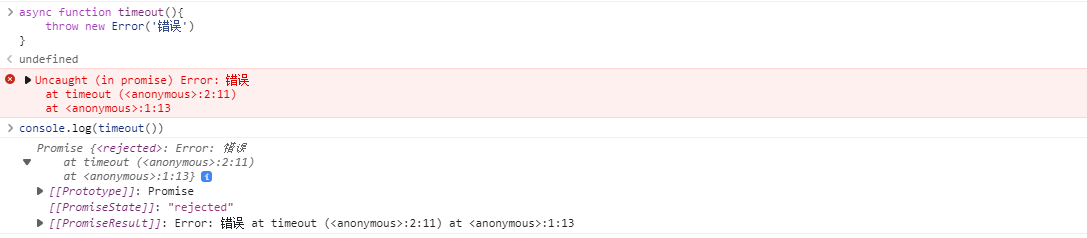
但如果timeout 函数内部抛出错误呢?
函数内部抛出错误处理
async function timeout() {
throw new Error('rejected');
}
console.log(timeout());就会调用Promise.reject() 返回一个promise 对象
那么要想获取到async 函数的执行结果,就要调用promise的then 或catch 来给它注册回调函数
async function timeout() {
return 'hello world'
}
timeout().then(result => {
console.log(result);
})如果async 函数执行完,返回的promise 没有注册回调函数,比如函数内部做了一次for 循环,你会发现函数的调用,就是执行了函数体,和普通函数没有区别,唯一的区别就是函数执行完会返回一个promise 对象
async function timeout() {
for (let index = 0; index < 3; index++) {
console.log('async '+ index);
}
}
console.log(timeout());
console.log('outer')async 关键字小结
async 关键字差不多了,最重要的就是async函数的执行会返回一个promise 对象,并且把内部的值进行promise的封装。如果promise对象通过then或catch方法又注册了回调函数,async函数执行完以后,注册的回调函数就会放到异步队列中,等待执行。
await 用法
如果只是async, 和promise 差不多,但有了await就不一样了, await 关键字只能放到async 函数里面,await是等待的意思,那么它等待什么呢,它后面跟着什么呢?其实它后面可以放任何表达式,不过我们更多的是放一个返回promise 对象的表达式,它等待的是promise 对象的执行完毕,并返回结果
现在写一个函数,让它返回promise 对象,该函数的作用是2s 之后让数值乘以2
// 2s 之后返回双倍的值
function doubleAfter2seconds(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(2 * num)
}, 2000);
} )
}现在再写一个async 函数,从而可以使用await 关键字, await 后面放置的就是返回promise对象的一个表达式,所以它后面可以写上 doubleAfter2seconds 函数的调用
async function testResult() {
let result = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
console.log(result);
}现在调用testResult 函数
testResult();打开控制台,2s 之后,输出了60
await 关键字小结
现在看看代码的执行过程,调用testResult 函数,它里面遇到了await, await 表示等待,代码就暂停到这里,不再向下执行了,它等待后面的promise对象执行完毕,然后拿到promise resolve 的值并进行返回,返回值拿到之后,它继续向下执行。具体到 我们的代码, 遇到await 之后,代码就暂停执行了, 等待doubleAfter2seconds(30) 执行完毕,doubleAfter2seconds(30) 返回的promise 开始执行,2秒 之后,promise resolve 了, 并返回了值为60, 这时await 才拿到返回值60, 然后赋值给result, 暂停结束,代码继续执行,执行 console.log语句。
就这一个函数,我们可能看不出async/await 的作用,如果我们要计算3个数的值,然后把得到的值进行输出呢?
async function testResult() {
let first = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
let second = await doubleAfter2seconds(50);
let third = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
console.log(first + second + third);
}6秒后,控制台输出220, 我们可以看到,写异步代码就像写同步代码一样了,再也没有回调地域了。
这里强调一下等待,当js引擎在等待promise resolve 的时候,它并没有真正的暂停工作,它可以处理其它的一些事情,如果我们在testResult函数的调用后面,console.log 一下,你发现 后面console.log的代码先执行。
async function testResult() {
let first = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
let second = await doubleAfter2seconds(50);
let third = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
console.log(first + second + third);
}
testResult();
console.log('先执行');例子扩展
再写一个真实的例子,我原来做过一个小功能,话费充值,当用户输入电话号码后,先查找这个电话号码所在的省和市,然后再根据省和市,找到可能充值的面值,进行展示
为了模拟一下后端接口,我们新建一个node 项目。 新建一个文件夹 async, 然后npm init -y 新建package.json文件,npm install express –save 安装后端依赖,再新建server.js 文件作为服务端代码, public文件夹作为静态文件的放置位置, 在public 文件夹里面放
index.html 文件, 整个目录如下
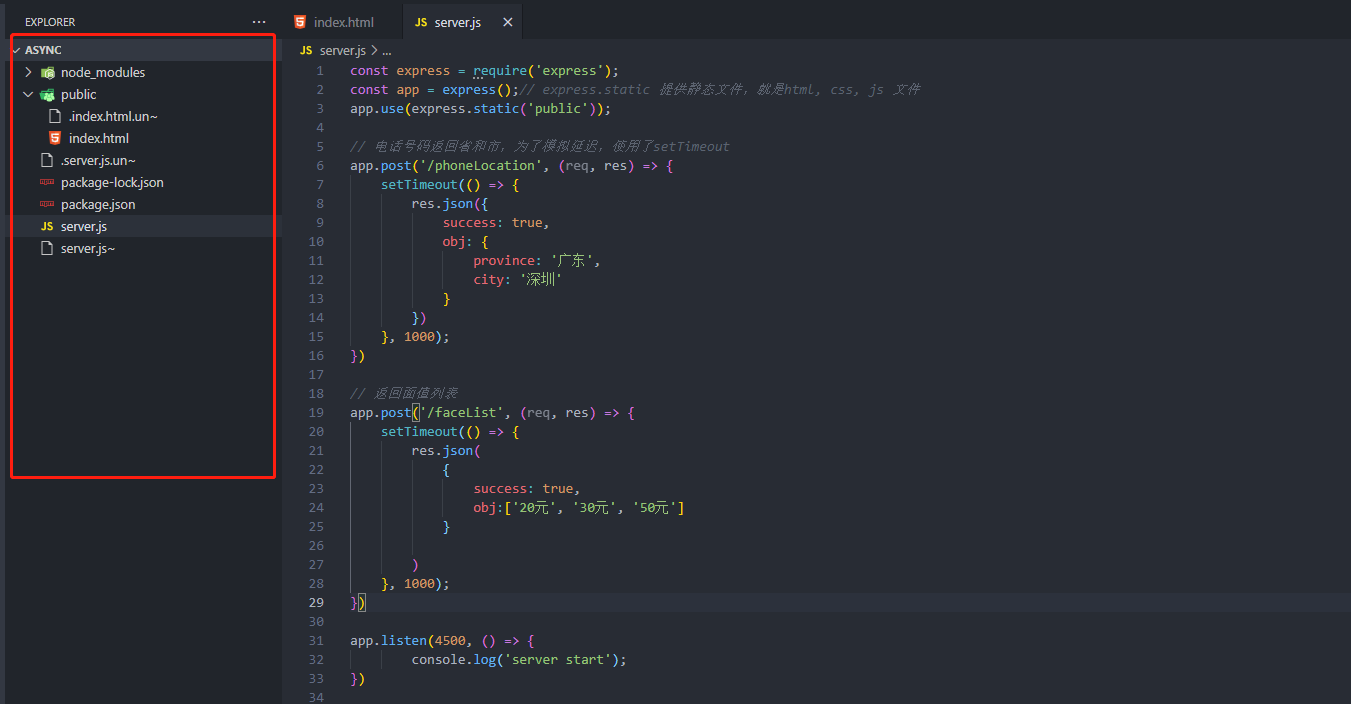
server.js 文件如下,建立最简单的web 服务器
const express = require('express');
const app = express();// express.static 提供静态文件,就是html, css, js 文件
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server start');
})再写index.html 文件,我在这里用了vue构建页面,用axios 发送ajax请求, 为了简单,用cdn 引入它们。 html部分很简单,一个输入框,让用户输入手机号,一个充值金额的展示区域, js部分,按照vue 的要求搭建了模版
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Async/await</title>
<!-- CDN 引入vue 和 axios -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 输入框区域 -->
<div style="height:50px">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入电话号码" v-model="phoneNum">
<button @click="getFaceResult">确定</button>
</div>
<!-- 充值面值 显示区域 -->
<div>
充值面值:
<span v-for="item in faceList" :key='item'>
{{item}}
</span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- js 代码区域 -->
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
phoneNum: '12345',
faceList: ["20元", "30元", "50元"]
},
methods: {
//获取到城市信息
getLocation(phoneNum) {
return axios.post('phoneLocation', {
phoneNum
})
},
// 获取面值
getFaceList(province, city) {
return axios.post('/faceList', {
province,
city
})
},
// getFaceResult() {
// this.getLocation(this.phoneNum)
// .then(res => {
// if (res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
// let province = res.data.obj.province;
// let city = res.data.obj.city;
// this.getFaceList(province, city)
// .then(res => {
// if (res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
// this.faceList = res.data.obj
// }
// })
// }
// })
// .catch(err => {
// console.log(err)
// })
// }
// async getFaceResult() {
// let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
// if (location.data.success) {
// let province = location.data.obj.province;
// let city = location.data.obj.city;
// let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
// if (result.data.success) {
// this.faceList = result.data.obj;
// }
// }
// }
async getFaceResult() {
try {
let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
if (location.data.success) {
let province = location.data.obj.province;
let city = location.data.obj.city;
let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
if (result.data.success) {
this.faceList = result.data.obj;
}
}
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>为了得到用户输入的手机号,给input 输入框添加v-model指令,绑定phoneNum变量。展示区域则是 绑定到faceList 数组,v-for 指令进行展示, 这时命令行nodemon server 启动服务器,如果你没有安装nodemon, 可以npm install -g nodemon 安装它。启动成功后,在浏览器中输入 http://localhost:3000, 可以看到页面如下, 展示正确

现在我们来动态获取充值面值。当点击确定按钮时, 我们首先要根据手机号得到省和市,所以写一个方法来发送请求获取省和市,方法命名为getLocation, 接受一个参数phoneNum , 后台接口名为phoneLocation,当获取到城市位置以后,我们再发送请求获取充值面值,所以还要再写一个方法getFaceList, 它接受两个参数, province 和city, 后台接口为faceList,在methods 下面添加这两个方法getLocation, getFaceList
methods: {
//获取到城市信息
getLocation(phoneNum) {
return axios.post('phoneLocation', {
phoneNum
})
},
// 获取面值
getFaceList(province, city) {
return axios.post('/faceList', {
province,
city
})
},
// 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表
getFaceResult () {
}
}现在再把两个后台接口写好,为了演示,写的非常简单,没有进行任何的验证,只是返回前端所需要的数据。Express 写这种简单的接口还是非常方便的,在app.use 和app.listen 之间添加如下代码
// 电话号码返回省和市,为了模拟延迟,使用了setTimeout
app.post('/phoneLocation', (req, res) => {
setTimeout(() => {
res.json({
success: true,
obj: {
province: '广东',
city: '深圳'
}
})
}, 1000);
})
// 返回面值列表
app.post('/faceList', (req, res) => {
setTimeout(() => {
res.json(
{
success: true,
obj:['20元', '30元', '50元']
}
)
}, 1000);
})最后是前端页面中的click 事件的getFaceResult, 由于axios 返回的是promise 对象,我们使用then 的链式写法,先调用getLocation方法,在其then方法中获取省和市,然后再在里面调用getFaceList,再在getFaceList 的then方法获取面值列表,
// 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表
getFaceResult () {
this.getLocation(this.phoneNum)
.then(res => {
if (res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
let province = res.data.obj.province;
let city = res.data.obj.city;
this.getFaceList(province, city)
.then(res => {
if(res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
this.faceList = res.data.obj
}
})
}
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}现在点击确定按钮,可以看到页面中输出了 从后台返回的面值列表。这时你看到了then 的链式写法,有一点回调地域的感觉。现在我们在有async/ await 来改造一下。
首先把 getFaceResult 转化成一个async 函数,就是在其前面加async, 因为它的调用方法和普通函数的调用方法是一致,所以没有什么问题。然后就把 getLocation 和
getFaceList 放到await 后面,等待执行, getFaceResult 函数修改如下
// 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表
async getFaceResult () {
let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
if (location.data.success) {
let province = location.data.obj.province;
let city = location.data.obj.city;
let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
if (result.data.success) {
this.faceList = result.data.obj;
}
}
}现在代码的书写方式,就像写同步代码一样,没有回调的感觉,非常舒服。
现在就还差一点需要说明,那就是怎么处理异常,如果请求发生异常,怎么处理? 它用的是try/catch 来捕获异常,把await 放到 try 中进行执行,如有异常,就使用catch 进行处理。
async getFaceResult () {
try {
let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
if (location.data.success) {
let province = location.data.obj.province;
let city = location.data.obj.city;
let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
if (result.data.success) {
this.faceList = result.data.obj;
}
}
} catch(err) {
console.log(err);
}
}参考文章:用 async/await 来处理异步 – SamWeb – 博客园 (cnblogs.com)